- Venture capital is a type of investment that provides funding to startups and emerging companies
- Venture capital firms identify and invest in high-potential, innovative businesses with the goal of generating financial returns
- The capital can provide the resources and expertise needed to help startups grow, but it also carries risks for investors
Venture capital is a crucial source of funding for businesses looking to grow and scale their operations. It is a type of private equity financing provided by specialised firms or individual investors, who are willing to invest in a business in exchange for an equity stake. In other words, businesses seeking venture capital must give up a percentage of their company in exchange for the funding and support needed to grow and succeed.
This article will provide an in-depth look at how venture capital works, including the process of raising venture capital, the various types of venture capital firms and investors, and the role of venture capital in the startup ecosystem. It will also discuss the potential risks and rewards of venture capital for businesses and investors, and provide case studies of successful venture capital investments. Additionally, it will explore the factors that can affect venture capital and the future outlook for this important source of funding.
What Is Venture Capital?
Venture capital is a type of funding that provides money for startups and businesses with growth potential. In exchange, the investor gets a percentage ownership stake in the company. This allows them to share any future profits (and losses) generated by that business.

The goal of venture capitalists is to make significant returns on their investments, which may mean selling the business for millions or billions of dollars or taking it public on the stock market. Startups and entrepreneurs, even established businesses that need a cash infusion, often go to venture capitalists when they need funding. Venture capitalists have the resources and expertise to evaluate new businesses and determine they’re worth investing in.
Importance of Capital Venture in The Economy
In the world of startups, venture capital is the lifeblood of innovation. Without it, many new businesses wouldn’t be able to get off the ground—and those that do would be forced to operate on a much smaller scale. Venture capital is essential to helping entrepreneurs turn their ideas into reality by funding research, development and marketing costs that help grow a nation’s economy.
Also, in the economy, venture capital is instrumental in creating jobs. By funding new businesses, venture capital provides a source of jobs for startup employees and independent contractors. And as those businesses grow, they create additional jobs by hiring more people as their operations expand.
Furthermore, venture capital firms help fund research and development in new technologies, which improve productivity and drive economic growth. This leads to more efficient production, increasing competitiveness and driving down consumer prices.
Lastly, venture capital firms also provide opportunities for individuals and businesses to expand their operations in the economy. Venture capital firms provide entrepreneurs with the money needed to get off and advice and connections to help them grow their businesses into thriving enterprises. They do this through networking and connecting entrepreneurs with other professionals in the venture capital industry.
How Does Venture Capital Work?
For venture capital to work, the venture capitalist needs to have access to capital to invest. That means the venture capitalist needs to have funds or access to other people’s funds. Venture capitalists are typically large institutions like pension funds, endowments, insurance companies, family offices and other institutional investors known as ‘limited partners.’
Venture capitalists typically invest in companies that have already launched and are looking to grow. They want to see strong management teams with a long track record of success and experience building businesses like the one they’re investing in. Different venture capital firms have different strategies and will focus on specific types of investments which helps make them work. These stages include investing in the following:
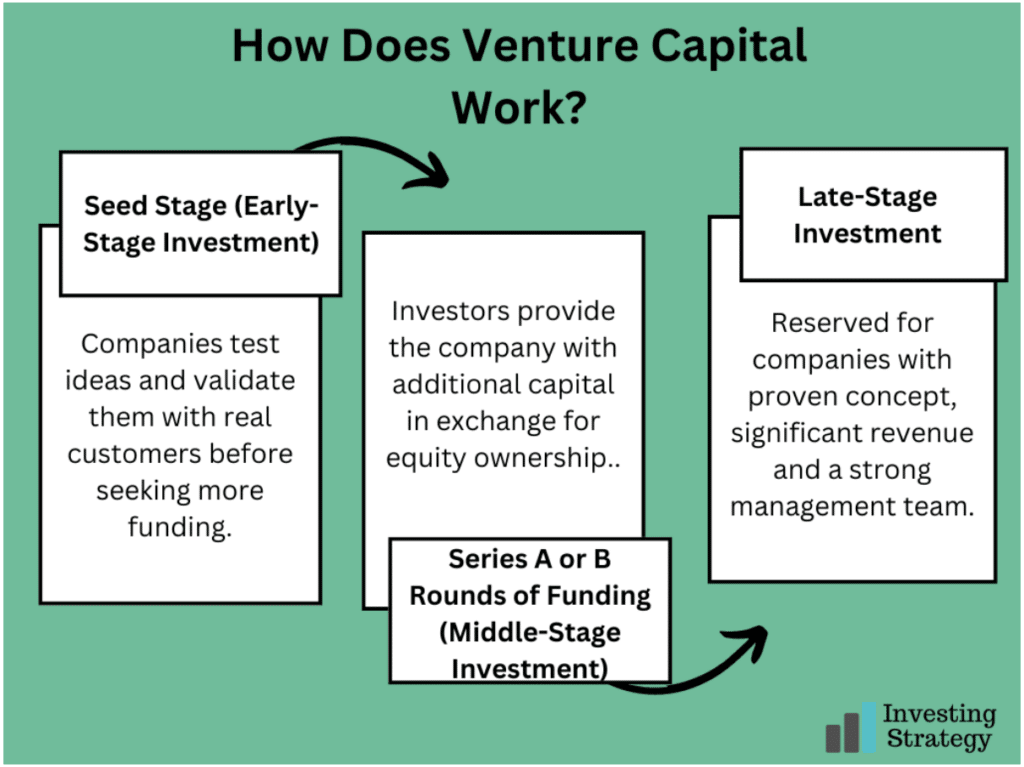
1. Seed Stage (Early-Stage Investment)
This is the earliest stage of funding, where venture capitalists provide seed capital to startups and businesses just starting. This stage aims for companies to test their ideas and validate them with real customers before seeking more funding from other sources. Venture Capitalists usually invest in companies at this stage because they believe in the business idea’s potential but need help getting it off the ground. Seed money is used for many things, including hiring employees or consultants in specific areas like marketing or technology development.
2. Series A or B Rounds of Funding (Middle-Stage Investment)
When a company has proven its business model with real customers, it’s time for venture capitalists to get involved. This is the middle stage of funding, where investors will provide the company with additional capital in exchange for equity ownership. The goal of this round is to help accelerate growth and expand operations. In exchange for their investment, VCs will take a seat on the board of directors and help determine the company’s strategic direction.
Once again, investors are looking for evidence of a market for their product or service and solid financial projections showing how much revenue they expect to generate within the next 2-3 years.
3. Late-Stage Investment
Late-stage investments are the final stage of funding, and they’re typically reserved for companies that have proven their concept, generated significant revenue and have a strong management team. VCs will take an even more significant equity stake in your company in exchange for their investment. Also, VCs are likely to exit at this stage when they perceive or see signs that the company can function as a standalone entity for them to sell their shares and generate income from their investment.
Venture capitalists don’t only raise funds for businesses; they also give businesses advice, mentorship and support. Different venture capitalists have different industries they invest in based on their guidelines. Some focus on technology companies, while others specialise in real estate investment.
Sources of Venture Capital
Sources of funding available to venture capitalists are numerous. But to be specific, venture capitalists can get funding from:
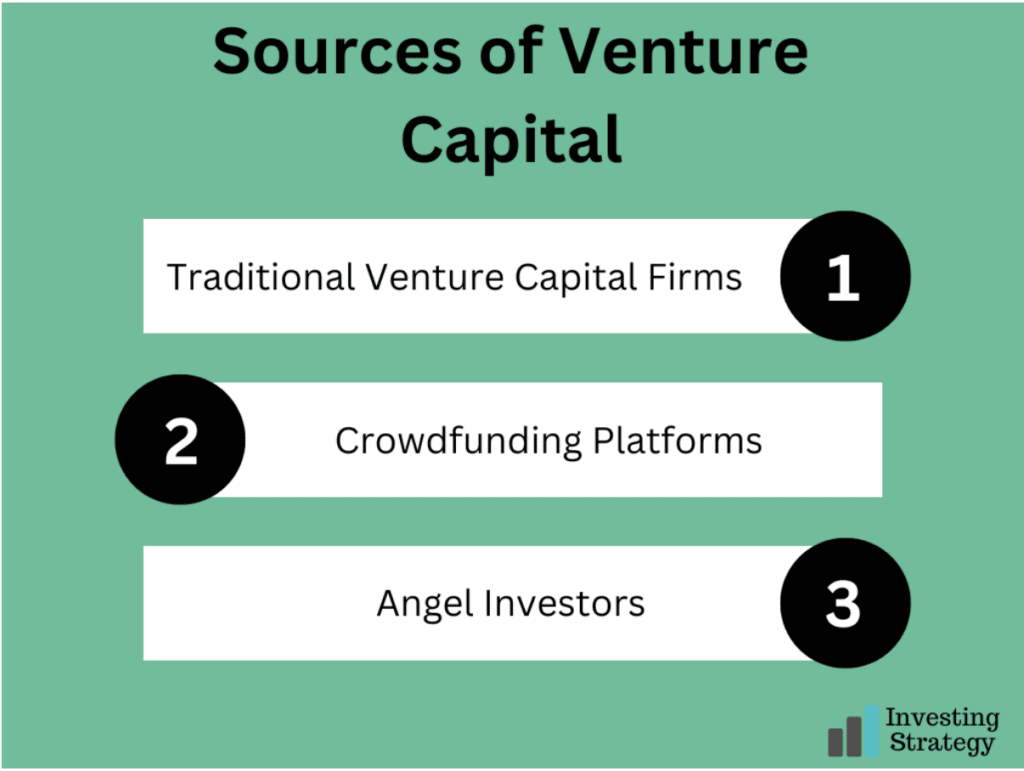
1. Traditional Venture Capital Firms
These include venture capital firms, investment banks, insurance companies, family offices and other investment institutions which provide funding to companies in exchange for an equity stake. The traditional venture capital firm is a professional partnership that invests in private companies. They are typically investors with a track record of successful investments, providing capital, advice, and connections to the firm’s portfolio companies.
2. Crowdfunding Platforms
Venture capitalists also get funding from the crowd. Crowdfunding platforms let companies raise capital from many investors through online platforms such as Kickstarter, GoFundMe, Indiegogo and more. For example, GoFundMe is a crowdfunding platform that lets entrepreneurs raise funds for their projects and offers rewards to backers who support them. Many projects have been funded through crowdfunding platforms.
3. Angel Investors
Angel investors are high-net-worth individuals who provide capital for a venture through their funds or by acting as intermediaries for other investors. Angel investors typically focus on seed and early-stage companies, providing funding to help them grow into more mature companies ready for venture capital funding.
Risks Involved in Venture Capital
There are many risks involved in venture capital. Some of these include:
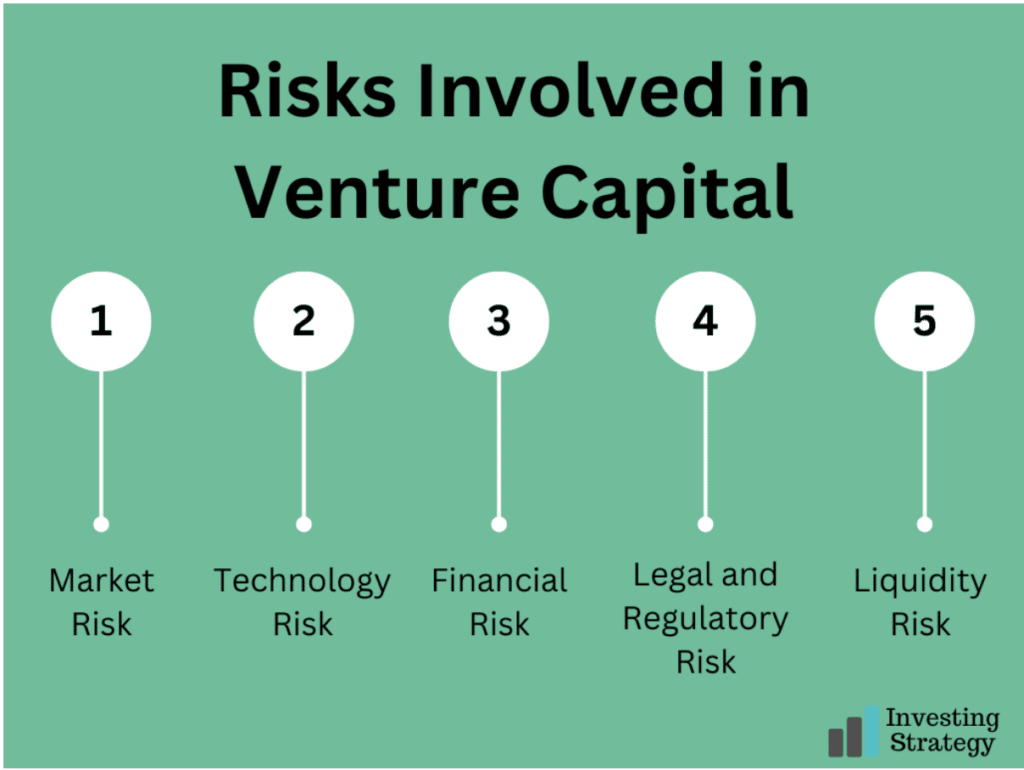
1. Market Risk
In venture capital, market risk involves the risk that the market for your product or service will not develop as you expect. For example, if your company’s product market is too small to be profitable, it might not be a good investment for venture capitalists.
2. Technology Risk
In venture capital, the technology risk is the risk that your company’s product will not perform as expected or will outperform a competitor’s product. If you have developed a new type of software, for example, but it doesn’t work as well as another company’s product on the market, it may not be a good investment for venture capitalists.
3. Financial Risk
In venture capital, the financial risk is the risk that your company will not be able to generate enough revenue to make a profit. This could mean that you have developed an innovative product but need to sell it for more money or have a large enough market share.
4. Legal and Regulatory Risk
One of the most common types of risk in venture capital is legal and regulatory. This means that changes in the law or changes in how regulators interpret the law could make your business unprofitable or illegal. For example, if you’re a company that relies on patents to protect its intellectual property, any changes in patent law could cause your business model to fail.
5. Liquidity Risk
Venture capitalists may find liquidating their investment in a business challenge. This means that the firm may need more time to sell its shares in the business. If this happens, it could have severe consequences for your company’s survival and venture capitalists’ returns on investment.
Factors Affecting Venture Capital Investment
The significant factors that affect venture capital investment include:
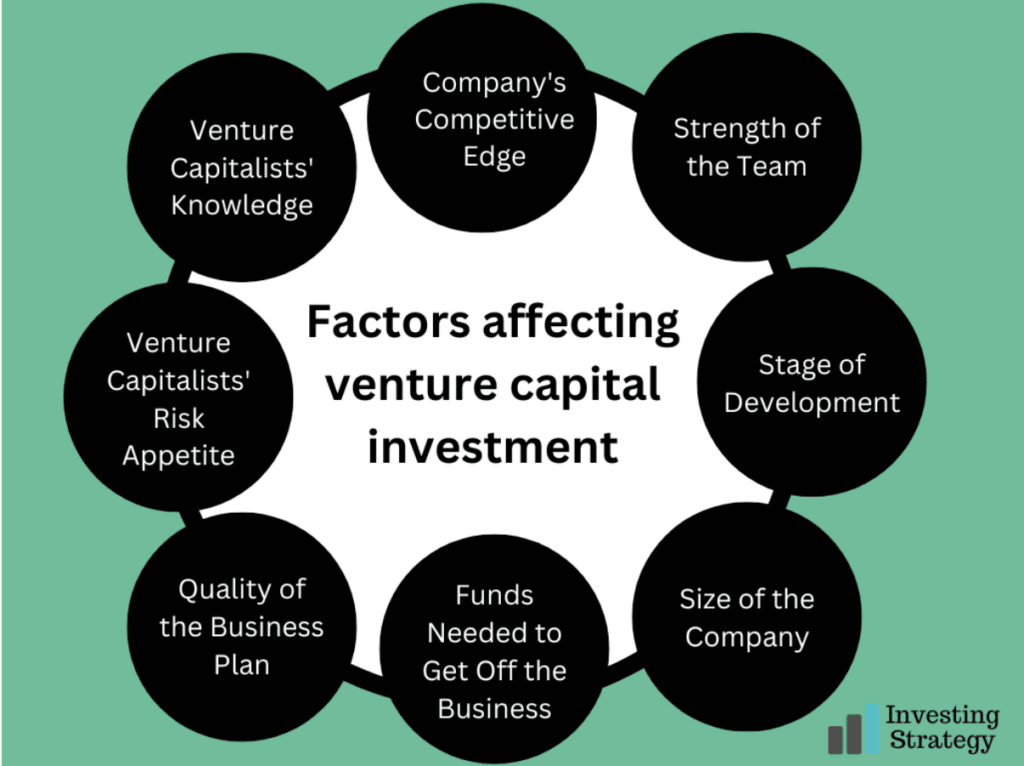
1. The Company’s Competitive Edge
The company’s competitive edge is a significant factor in determining whether or not venture capitalists will invest in it. This can be the company’s product, service or technology and its ability to differentiate itself from competitors.
2. The Venture Capitalists’ Knowledge of Your Industry
A venture capitalist with good knowledge of your industry can make or break a company’s ability to raise capital. If the investor is knowledgeable about your industry, they’ll know what type of companies succeed in it and which ones fail. This knowledge can help them make better decisions about whether or not to invest in your startup.
3. The Venture Capitalists’ Risk Appetite
A venture capitalist’s risk appetite is the amount of risk they’re willing to take when investing in a company. Some investors may be more interested in only investing in companies guaranteed to succeed, while others will take more risks with their investment and hope they hit it big.
4. The Quality of the Business Plan
The quality of the business plan is essential in determining whether or not a venture capitalist will invest in your startup. The more detailed and well-written it is, the better. The more clearly you have outlined your goals, strategies for achieving them, financial forecasts and market research, the more likely you will get an investor’s attention.
5. Funds Needed to Get Off the Business
The amount of money you will need to get your business off the ground is another critical factor that venture capitalists consider. They want to know how much capital they will have to invest to see a return on their investment.
6. The Size of the Company
The company’s size is another essential factor that venture capitalists will consider when deciding whether or not to invest in your startup. They want to know if there is room for growth from a financial and market perspective. They also want to know how large your business will become over time and how it will affect their potential profits.
7. The Stage of Development
The stage of development is also a factor that venture capitalists consider when deciding whether or not to invest in your startup. They want to know how far along you are in the process and whether or not they can help move things forward. The more developed your company is, the easier it will be for them to see how much money they can make from their investment.
8. The Strength of the Team
One of the essential things for venture capitalists to consider is the strength of their team. They want to know that you have a solid group of people capable of bringing your idea into reality and making it successful. The more experienced and knowledgeable they are, the better your chance of getting funding.
Advantages of Venture Capital
The decision to seek venture capital can be a good one. These include:
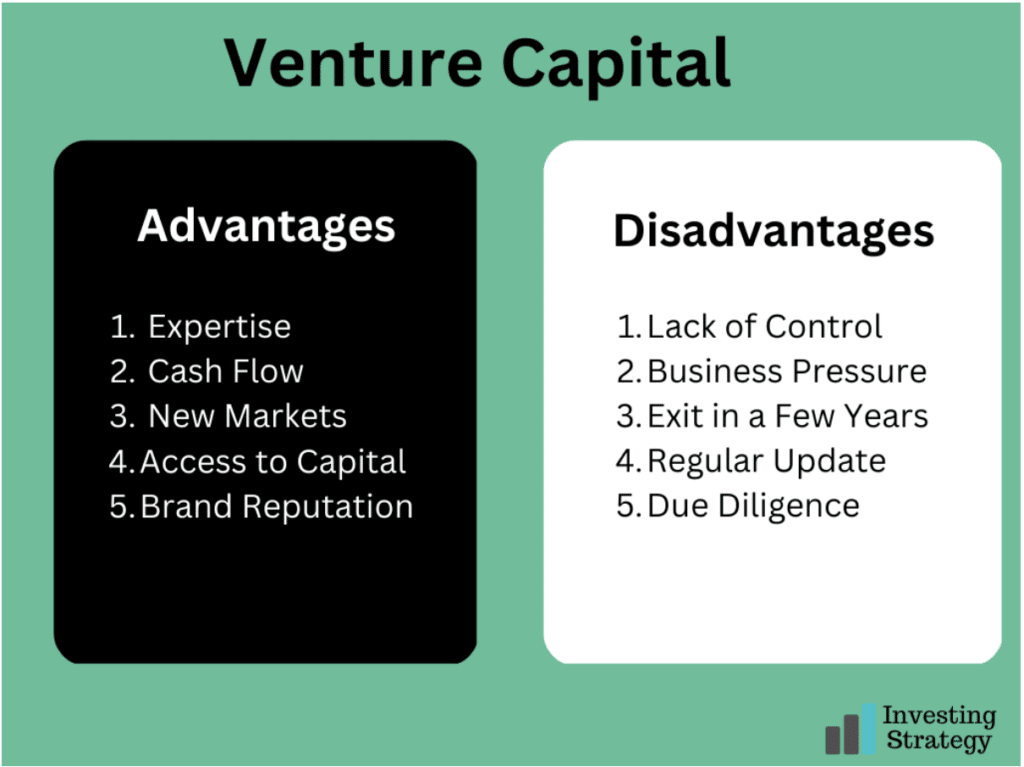
1. Access to Expertise
When you have venture capitalists on board, they can give your company access to their expertise. This can help you avoid mistakes that could cost you a lot of money in the long run.
2. Increased Cash Flow
Venture capital can help you access much more tremendous cash than you might otherwise have. This can allow you to expand your business in ways that might not have been possible without this extra funding.
3. Access to New Markets
Venture capitalists often have connections with people in high places who can help expand their reach into new markets. They also know how to make money and can offer advice on how to do so effectively.
4. Access to Capital Without Collaterals
If you are a startup company, you may need more collateral to secure loans from banks. However, venture capitalists can provide you with capital that doesn’t require collateral.
5. Improved Business Reputation
Access to venture capital can improve your reputation as an entrepreneur by showing that other people believe in you and your company’s future.
Venture Capital Disadvantages
If you take on venture capital, here are the downsides of doing so:
1. Lack of Control
One of the major disadvantages of taking on venture capital is that you will lose some control over your company. If you take on venture capital, you may only be able to make some decisions regarding the direction of your business because investors will want to be consulted for them to feel that their money is being put to good use.
2. Increased Pressure on Your Business
Once you accept venture capital, there is a lot of pressure to succeed. This can be very stressful and lead to difficult decisions that may not be in the best interest of your company.
3. They Exit in a Few Years
Venture capitalists are only interested in investing in your company for a few years before they exit. This means they want to see you grow quickly and then sell their stake in the company at a profit. In other words, to keep the business going, you’ll need to find another investor or buyer.
4. Time-To-Time Update
To receive venture capital, you may have to agree to a time-to-time update with the investor. This means that they will expect regular updates on your company’s progress and finances so that they can decide whether to continue investing or sell their stake in your business.
5. Due Diligence
One of the most significant disadvantages of taking on venture capital is that you will have to go through a lot of due diligence. This is a process by which venture capitalists look into your financial statements, business plan, and other aspects of your company to determine whether or not they want to invest in it. If you are not prepared for this process, it can be challenging to get through it effectively.
Case Studies of Successful Venture Capital Investments
To get a better idea of what a venture capital company looks for in an investment, it’s essential to look at some examples of successful investments.
One good example is Facebook. Mark Zuckerberg started this company while he was still in college, and it quickly grew to become one of the world’s most popular social media networks. He secured venture capital funding from Accel Partners, Greylock Partners and Meritech Capital, allowing him to continue growing his company after graduating from school.
Another example is Uber Technology. Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp started this company in 2009 with the idea of creating a taxi service that could be accessed through a mobile application. They were able to secure funding from Benchmark Capital and First Round Capital, which helped them grow the company into one of the most popular transportation services in the world.
These two examples show how venture capital investments can help startups grow into large corporations worth billions of dollars.
What is the Future Outlook for Venture Capital?
The venture capital industry is expected to remain strong in the coming years, with more companies receiving funding from investors and becoming profitable. The industry will also grow as new companies are formed, giving investors more opportunities to profit from their investments.
Moreover, venture capitalists are quick to invest in emerging technologies and industries, which gives them the ability to profit from these trends, which is quite positive. Therefore, as long as new ideas are being developed and brought to market, there will be a need for venture capital investments.